One of the most common complications for sexually active people is not having genital warts or HPV. Due to the nature of infection and the rapid spread of HPV, you may become infected during your first sexual contact with an infected person. Therefore, in addition to safe sex, you should get the HPV or genital warts vaccine before having sex. In the following, you will learn more about these complications, their symptoms and treatment methods:
What is a genital wart?
Genital warts are the most common type of sexually transmitted infection caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus is transmitted by direct skin-to-skin contact with people infected with HPV. HPV is transmitted from person to person during vaginal and anal intercourse. It is also sometimes transmitted through oral sex.
How do you get genital warts?
30 to 40 strains of HPV specifically affect the genitals, but only a few of these strains cause genital warts. You get genital warts when your genitals come into contact with the genitals of another person who has HPV. Your partner may have HPV, but you may not see any symptoms.
Even if you use a condom or don’t have penetrative sex, you can still get warts. This is because condoms do not completely cover the skin of the genitals. Genital warts are usually caused by strains of HPV, which are different from the strains that cause warts on the hands or other parts of the body.
What are the symptoms of genital warts in men and women?
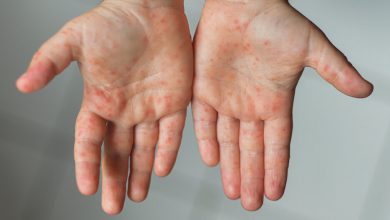
Genital warts are transmitted through sexual activity, including oral, vaginal, and anal sex. Your symptoms may appear weeks or months after infection. Also, genital warts are not always visible to the human eye. They may be very small, skin-colored, or slightly darker. The top of the growth looks like cauliflower and may look smooth or slightly bulky to the touch.
The growths may appear as a group of warts or just warts. If genital warts spread or enlarge, this condition can be uncomfortable or painful.
Genital warts in men can occur in the following areas:
- rod
- testicular cyst
- groin
- In or around the anus
Genital warts in women usually occur in the following areas:
- Inside the vagina or anus
- around the vagina or anus
- in the cervix
Even if you don’t see genital warts, you may experience the following symptoms:
- vaginal discharge
- Itchy
- bleeding
- mite
Genital warts may appear on the lips, mouth, tongue, or throat of a person who has oral sex with an HPV partner.
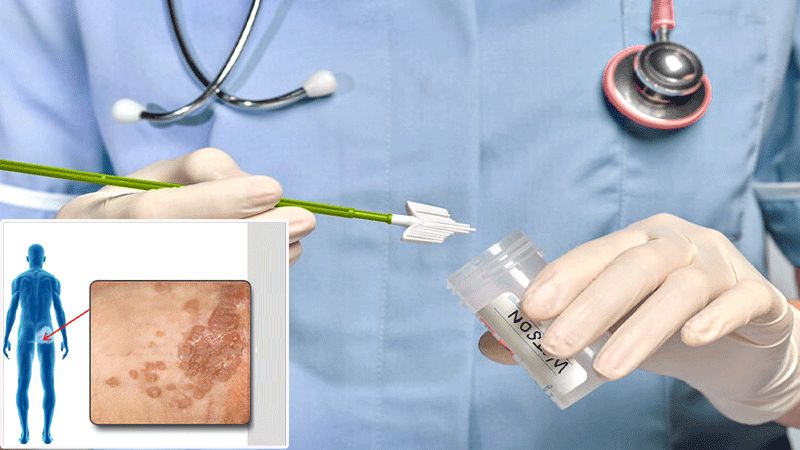
Diagnosis of genital warts in men and women
To diagnose this complication in men and women, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist, urologist and general surgeon to confirm the presence of these warts. Because in some cases these bumps are misdiagnosed with other serious diseases such as cancer. Here are some ways to diagnose the disease:
- Visual examination for warts with a magnifying glass
- Sampling of the appendix under anesthesia to diagnose the type of virus that causes the disease
Female genital warts are easier to diagnose than they are in men. If you think you may have these side effects, you should consult your gynecologist. If there are obvious symptoms in and around the vagina, they can be detected by regular examination.
To view the full article on genital warts in men and women, you can refer to the relevant link.
The vagina and uterus can also be examined with a device or a Pap smear, and if in doubt, the sample is examined in a pathology laboratory.
Risk factors for genital warts
Anyone who is sexually active is at risk of contracting HPV. However, the risk of developing genital warts increases in the following cases:
- She has many sexual partners
- Their safety is weak
- He is less than 30 years old
- They also have other sexually transmitted diseases
How are genital warts treated?
Visible genital warts usually disappear over time, and HPV itself can remain in skin cells. This means that you may encounter these complications several times in your life.
So if you want to prevent the virus from spreading to others, managing your symptoms is very important. This is because genital warts can spread to others, even if there are no visible warts or other symptoms. The type of treatment you get depends on the appearance and location of the wart. Your doctor or nurse will talk to you about this. This disease is considered dangerous because it increases the risk of cervical and penile cancer. Some treatments for these side effects include:
ointment or medicine
You can use some prescription topical medications to get rid of genital warts. Of course, these medications are not definitive methods of removing genital warts and are only used for small, mild to moderate treatments. Some of the medicines used to treat these side effects are:
- podophyllin ointment
- the house
- salicylic acid
Laser Genital Warts Method
Laser can be used to get rid of this disease. Laser surgery is usually done on an outpatient basis in an office or clinic by a specialist and does not require anesthesia. This technique is used as a definitive treatment to relieve the symptoms of genital warts. In the laser method, by direct radiation to the growths, the wart tissue is removed and the laser radiation is corrected.
This technique is also used for large or large warts and usually one session is sufficient to treat warts with a laser.
Freeze, freeze, or freeze
Most doctors use liquid nitrogen, which can reach -320 degrees Fahrenheit, to freeze warts. In this method, doctors freeze the warts by spraying liquid nitrogen on the growths. Sometimes the treatment is repeated several times and may be accompanied by pain and blisters.
electrician
To treat genital warts by the electrocautery method, an electric current is used to burn the appendages under local anesthesia and the appendix is removed in one session. In this method, the wart tissue is removed from the heat with a sharp, needle-like instrument.
What are the possible side effects of HPV?
Genital warts are a low-risk type of HPV infection. High-risk strains such as HPV 16 and HPV 18 are involved in most cervical cancers. They can cause early changes in the cells of the cervix called dysplasia.
Other types of HPV can also cause vulvar cancer. They may also have the following side effects:
- Penile cancer
- anal cancer
- Throat Cancer
- esophageal cancer
* Advertising Report